Page 112 - 14_Atti_SIN_SNO_2022_flip
P. 112
Proceedings SNO “Percorsi clinici in Neuroscienze”
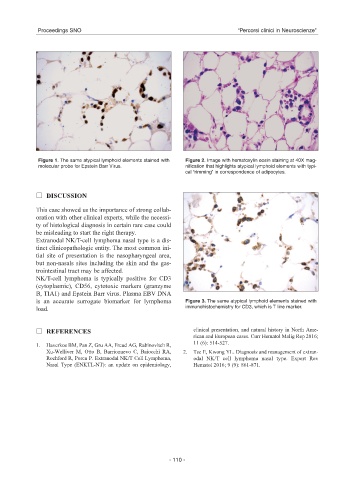
Figure 1. The same atypical lymphoid elements stained with Figure 2. Image with hematoxylin eosin staining at 40X mag-
molecular probe for Epstein Barr Virus. nification that highlights atypical lymphoid elements with typi-
cal “rimming” in correspondence of adipocytes.
DISCUSSION
This case showed us the importance of strong collab-
oration with other clinical experts, while the necessi-
ty of histological diagnosis in certain rare case could
be misleading to start the right therapy.
Extranodal NK/T-cell lymphoma nasal type is a dis-
tinct clinicopathologic entity. The most common ini-
tial site of presentation is the nasopharyngeal area,
but non-nasals sites including the skin and the gas-
trointestinal tract may be affected.
NK/T-cell lymphoma is typically positive for CD3
(cytoplasmic), CD56, cytotoxic markers (granzyme
B, TIA1) and Epstein Barr virus. Plasma EBV DNA
is an accurate surrogate biomarker for lymphoma Figure 3. The same atypical lymphoid elements stained with
load. immunohistochemistry for CD3, which is T line marker.
REFERENCES clinical presentation, and natural history in North Ame-
rican and European cases. Curr Hematol Malig Rep 2016;
1. Haverkos BM, Pan Z, Gru AA, Freud AG, Rabinovitch R, 11 (6): 514-527.
Xu-Welliver M, Otto B, Barrionuevo C, Baiocchi RA, 2. Tse E, Kwong YL. Diagnosis and management of extran-
Rochford R, Porcu P. Extranodal NK/T Cell Lymphoma, odal NK/T cell lymphoma nasal type. Expert Rev
Nasal Type (ENKTL-NT): an update on epidemiology, Hematol 2016; 9 (9): 861-871.
- 110 -