Page 106 - 14_Atti_SIN_SNO_2022_flip
P. 106
Proceedings SNO “Percorsi clinici in Neuroscienze”
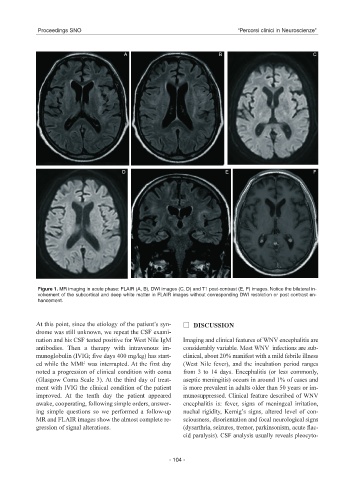
A B C
D E F
Figure 1. MR imaging in acute phase: FLAIR (A, B), DWI images (C, D) and T1 post-contrast (E, F) images. Notice the bilateral in-
volvement of the subcortical and deep white matter in FLAIR images without corresponding DWI restriction or post contrast en-
hancement.
At this point, since the etiology of the patient’s syn- DISCUSSION
drome was still unknown, we repeat the CSF exami-
nation and his CSF tested positive for West Nile IgM Imaging and clinical features of WNV encephalitis are
antibodies. Then a therapy with intravenous im- considerably variable. Most WNV infections are sub-
munoglobulin (IVIG; five days 400 mg/kg) has start- clinical, about 20% manifest with a mild febrile illness
ed while the MMF was interrupted. At the first day (West Nile fever), and the incubation period ranges
noted a progression of clinical condition with coma from 3 to 14 days. Encephalitis (or less commonly,
(Glasgow Coma Scale 3). At the third day of treat- aseptic meningitis) occurs in around 1% of cases and
ment with IVIG the clinical condition of the patient is more prevalent in adults older than 50 years or im-
improved. At the tenth day the patient appeared munosuppressed. Clinical feature described of WNV
awake, cooperating, following simple orders, answer- encephalitis is: fever, signs of meningeal irritation,
ing simple questions so we performed a follow-up nuchal rigidity, Kernig’s signs, altered level of con-
MR and FLAIR images show the almost complete re- sciousness, disorientation and focal neurological signs
gression of signal alterations. (dysarthria, seizures, tremor, parkinsonism, acute flac-
cid paralysis). CSF analysis usually reveals pleocyto-
- 104 -